You know the feeling—staring at your cloud bill, wondering where all that money went, or watching your team juggle multiple dashboards just to get a clear picture of your infrastructure. You’re not alone. Every IT team eventually faces the same question: should you stick with Azure’s native tools, or invest in a third-party solution that claims to simplify everything?
The truth is, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. But there are key factors to consider that can help you make the right decision for your organization.
What You Get with Azure’s Built-In Tools
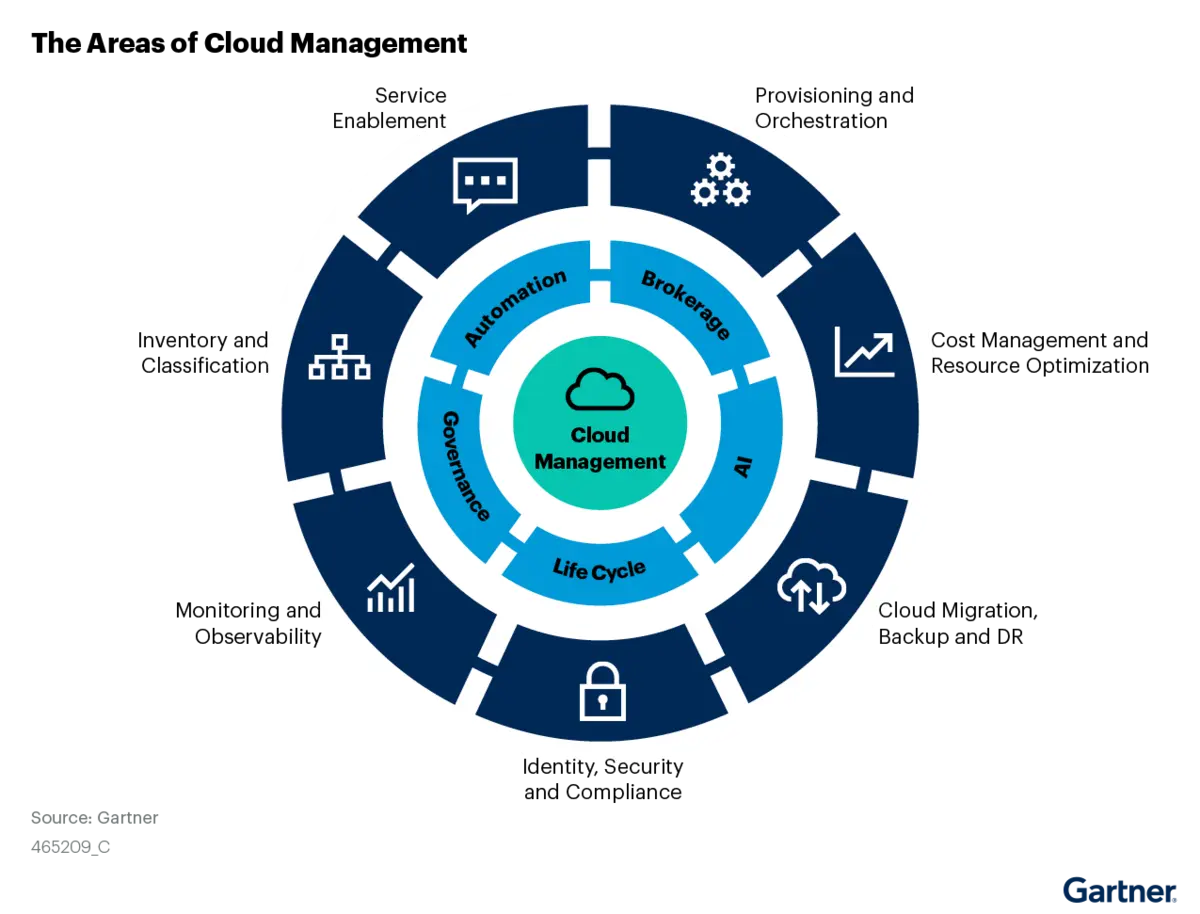
Azure offers a solid suite of built-in management tools right out of the box. The Azure Portal serves as your central dashboard, giving you a high-level view of your entire environment. Azure Monitor tracks system performance and alerts you to issues in real time, while Azure Cost Management provides detailed insights into your spending, helping you manage your budget more effectively.
These tools are highly effective—especially if your environment is fully committed to Microsoft. They update automatically, integrate seamlessly with Office 365, and your team is likely already familiar with how they work. Plus, because they run natively within Azure, they’re fast and optimized for performance.
However, there’s a limitation: these tools shine only when Azure is your entire cloud ecosystem. The moment you introduce AWS for a specific workload or Google Cloud for analytics, you’re back to juggling multiple dashboards and trying to piece together a cohesive view across platforms.
Why Third-Party Solutions Exist
Third-party cloud management solutions exist because most businesses don’t operate in a single-vendor environment. A robust cloud management platform provides a unified view across all your infrastructure—whether it’s Azure, AWS, Google Cloud, or even legacy on-premises servers that just won’t go away.
These tools often deliver capabilities that extend far beyond what native solutions offer. They enable true cross-platform automation, uncover hidden cost-saving opportunities, and provide governance frameworks tailored to your specific compliance needs—instead of requiring you to conform to theirs.
What sets them apart is their singular focus. While Microsoft has to juggle everything from operating systems to gaming consoles, these third-party providers are laser-focused on solving complex cloud management challenges—and it shows in the depth and flexibility of their solutions.
Performance vs. Capability Trade-offs
Azure’s native tools will almost always offer faster performance when managing Azure resources. That’s to be expected—they operate directly on the same infrastructure as your workloads. For routine, day-to-day tasks, this speed can translate into increased productivity for your team.
Third-party solutions may introduce slight performance delays, but they make up for it with broader capabilities and deeper insights. The trade-off, then, is between the speed of individual operations and the ability to gain unified, comprehensive visibility across your entire infrastructure. For most organizations—especially those operating in complex, multi-cloud environments—the analytical depth and cross-platform functionality of third-party tools outweigh the minor performance differences.
Integration Challenges and Opportunities
Your existing technology stack plays a critical role in determining the right cloud management approach. If your organization is deeply invested in Microsoft technologies—such as Active Directory, Office 365, and SQL Server—Azure’s native tools offer seamless integration. Security policies, user management, and compliance frameworks all work together effortlessly within the Microsoft ecosystem.

Third-party solutions, on the other hand, are built for broader compatibility. They’re designed to integrate with a wide range of platforms—not just Microsoft. This flexibility becomes especially valuable as your technology landscape evolves or as you onboard acquired companies that use different systems.
At SNP Technologies Inc., we’ve seen this evolution firsthand. Many of our clients begin with Azure-native tools but eventually require more expansive capabilities as their cloud strategies mature. Our comprehensive cloud management portal bridges that gap—offering deep Azure integration while enabling effective management across multi-cloud environments. This approach helps organizations maintain operational consistency, even as their technology portfolios grow increasingly diverse.
The Real Economics of Cloud Management
Pricing isn’t always as straightforward as it seems. Azure’s native tools may appear cost-effective because they’re bundled with your subscription. However, the true cost includes training your team, customizing workflows, and managing multiple disconnected tools—especially if your organization operates across different cloud platforms.
Third-party solutions typically come with separate licensing fees, but they often deliver a higher return on investment. Their advanced cost optimization features can offset licensing costs within months. By reducing operational overhead, these tools allow your team to focus on strategic initiatives rather than managing fragmented systems. Enhanced resource utilization across platforms frequently results in substantial long-term savings.
There’s also the opportunity cost to consider. How much productivity is lost as your team switches between multiple management interfaces? How many cost-saving or performance-enhancing opportunities are missed due to a lack of unified visibility across your infrastructure?
Making the Right Choice for Your Organization
Your decision should align with both your organization’s current needs and future goals. For businesses operating primarily within Azure, the native toolset may be sufficient for immediate requirements. However, organizations with multi-cloud environments, complex governance needs, or ambitious growth plans often find that specialized third-party platforms deliver significantly greater long-term value.
Consider where your organization will be in the next three years. Assess your team’s current skill sets and their capacity to adopt new tools. Evaluate your compliance obligations, operational complexity, and the scalability of your existing systems. The right solution should not only meet your present-day needs but also support your strategic vision as your business continues to evolve.
Ready to Optimize Your Cloud Management Strategy?
At SNP Technologies Inc., we understand that selecting the right cloud management approach is critical to your organization’s success. Our comprehensive cloud management portal delivers enterprise-grade capabilities with the flexibility modern businesses need to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Our platform provides unified visibility, intelligent automation, and advanced cost optimization—empowering organizations to maximize cloud investments while maintaining operational efficiency. With over 1,000 successful project implementations, 14 Microsoft specializations, and more than 150 certifications, we bring deep, proven expertise to every stage of your cloud transformation journey.
Contact us today to learn how our cloud management portal can address your specific challenges and support your strategic goals. Let’s explore how the right management approach can streamline your operations and drive measurable business outcomes.