Over the past few years, Continuous Delivery, Continuous Integration, and Continuous Delivery have become a part of our daily technology vocabulary. As we continue to implement these practices into our Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) workflows, these three terminologies can be confusing.
In this post, we will define each of these processes and how they work together so that stakeholders, developers and project managers can work in alignment in one integrated environment.
Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), and Continuous Deployment (CD) are essential practices in modern software development that enhance collaboration, speed, and quality. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences between them:
Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration is the process of automating the build and testing of code every time a team member commits changes to version control. CI encourages developers to share their code and unit tests by merging their changes into a shared version control repository after every small task completion. Committing code triggers an automated build system to grab the latest code from the shared repository and to build, test, and validate the full master branch. In the continuous integration process, most of the work is done by an automated test technique, which requires a unit test framework. It is a best practice to have a build server designed specifically for performing these tests, so your development team can continue merging requests even while tests are being performed. Implementing Continuous Integration is a best practice that enhances the development workflow, improves code quality, and accelerates the overall software delivery process. By automating the build and testing phases, development teams can focus more on writing code and less on integration issues, ultimately leading to a more efficient and collaborative environment.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous Delivery is a software development practice that ensures code changes are automatically prepared for release to production. It involves delivering every change to a production-like environment, where rigorous automated testing validates that applications and services function as expected. Continuous Delivery is a vital practice in modern software development that streamlines the deployment process while ensuring high quality. By automating the delivery pipeline and conducting thorough testing, organizations can achieve a state of readiness for production at any time, empowering them to respond swiftly to business needs and market demands. This practice not only enhances efficiency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement and collaboration within development teams.
Continuous Deployment
Every change that passes the automated tests is deployed to production automatically. Continuous deployment relies on small changes, which are constantly tested, deployed, and released to production immediately upon verification. The ownership of the code from development to release must be controlled by the developer and must be free-flowing. The automation of steps allows this process to be implemented and executed without cumbersome workflows. Post-deployment, logs must be inspected to validate whether any key metrics are affected—positively or negatively. Continuous deployment should be the goal of most companies that are not constrained by regulatory or other requirements.
Understanding these key differences is crucial for teams looking to implement effective DevOps practices. While CI focuses on integrating code and running tests, CD ensures that the software is always ready for deployment, and Continuous Deployment automates the release process. Together, these practices enable teams to deliver high-quality software quickly and efficiently.
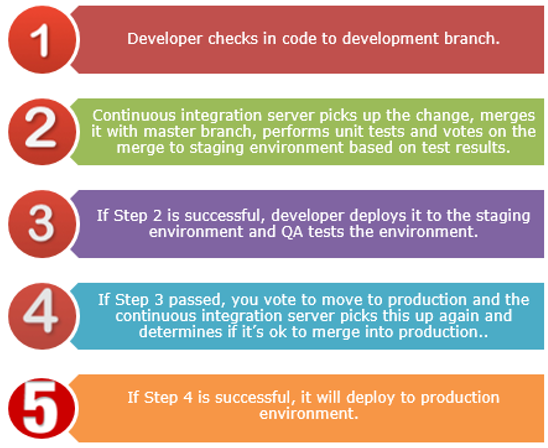
How they work together
When you’re ready for deployment, you need to have your automation in place. Automate your continuous integration build server and continuous delivery to staging, which gives you the ability to automatically deploy to production. This means you will automate the entire process from start to finish.
For more information about Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment, Contact SNP Technologies Here